Xylella fastidiosa temporal dynamics and spatial distribution
|
Diseases caused by the insect-transmitted bacterium Xylella fastidiosa have been reported in the Americas since the 19th century, causing primarily Pierce’s disease of grapevine, almond leaf scorch (ALS), and citrus variegated chlorosis. Here, we investigate the temporal and spatial distribution of the ALS disease. The objective of this work is to characterize the temporal and spatial distribution of ALS disease within infected orchards.
This project is in collaboration with Dr. Ofir Bahar (ARO) and Prof. Dani Shtienberg (ARO) Publication: Zecharia N, Krasnov H, Vanunu M, Castillo A, Siri AC, Haberman A, Dror O, Vakel L, Almeida RPP, Blank L, Shtienberg D and Bahar O (2022). Xylella fastidiosa outbreak in Israel: population genetics, host range and temporal and spatial distribution analysis. Phytopathology 112: 2253-2471 [pdf] Journal Link |
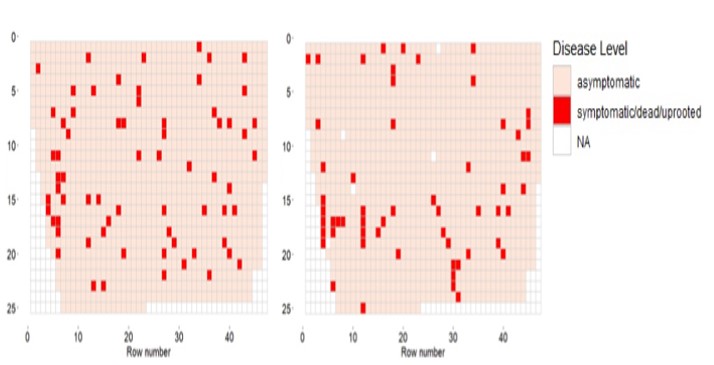
Long-term monitoring of almond leaf scorch (ALS). In each sub-figure, a representation of the status of infected plants in each year is given. Every square in the grid represents a tree and trees were categorized as symptomatic and asymptomatic trees. The X-axis represents the row number and the y-axis the tree number.
|
Land-use and water quality effects on microbiomes in lakes in Germany
|
We investigate the microbiomes of 46 lakes and evaluate how and to what extant human activities involved in shaping lakes microbiomes.
This project is in collaboration with Dr. Daniel Sher (University of Haifa). Publications: Marmen S, Man-Aharonovich D, Grossowicz M, Blank L, Yacobi Y and Sher DJ (2016). Distribution and habitat specificity of potentially-toxic Microcystis across climate, land and water use gradients. Frontiers in Microbiology 7: 271 [pdf] Journal Link Marmen S, Blank L, Al-Ashhab A, Malik A, Ganzert L, Lalzar L, Grossart HP and Sher DJ (2020). The role of land use types and water chemical properties in structuring the microbiomes of a connected lake system. Frontiers in Microbiology 11: 89 [pdf] Journal Link |